Introduction
Polymers are macromolecules composed of repeating units called monomers. They play a crucial role in our everyday lives, from the plastic bottles we use to the fabrics we wear. There are two main types of polymers: natural and synthetic. In this article, we will explore the differences between these two types and their respective properties.
Natural Polymers
Natural polymers are derived from living organisms and occur in nature. They are formed through biological processes and are often biodegradable.
Examples of natural polymers
- Proteins: Proteins are large molecules composed of amino acids. They are found in animals and plants and have various functions in the body.
- Cellulose: Cellulose is a polysaccharide found in the cell walls of plants. It provides structural support and is the main component of wood and cotton.
- DNA: DNA is a natural polymer that carries genetic information in living organisms.
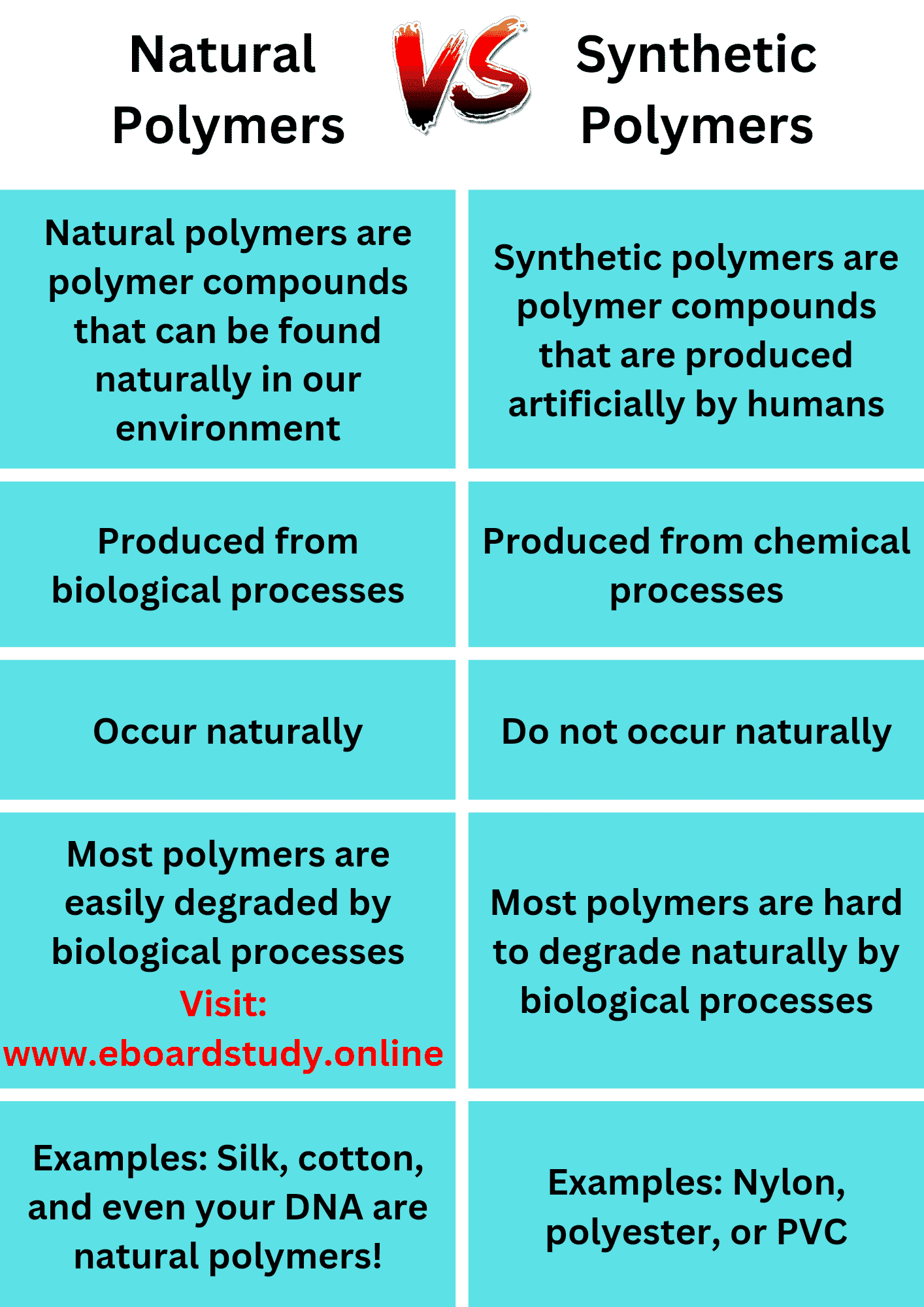
Synthetic Polymers
Synthetic polymers, on the other hand, are man-made and are derived from petrochemicals. They are created through chemical reactions and can have a wide range of properties depending on their composition.
Examples of synthetic polymers
- Polyethylene: Polyethylene is a common synthetic polymer used in packaging materials, plastic bags, and bottles. It is known for its flexibility and resistance to moisture.
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): PVC is a versatile synthetic polymer used in construction, healthcare, and electrical industries. It is durable and has excellent chemical resistance.
- Polystyrene: Polystyrene is a lightweight synthetic polymer used in packaging, insulation, and disposable food containers. It is known for its thermal insulation properties.
Differences between Natural Polymers and Synthetic Polymers
- Source: Natural polymers are derived from natural sources, while synthetic polymers are man-made.
- Biodegradability: Natural polymers are biodegradable, meaning they can be broken down by natural processes. Synthetic polymers, on the other hand, are non-biodegradable and can persist in the environment for a long time.
- Structure: Natural polymers have a more complex and varied structure compared to synthetic polymers, which are usually more uniform.
- Properties: Natural polymers often have unique properties specific to their source, while synthetic polymers can be engineered to have specific properties.
- Cost: Natural polymers are generally more expensive to produce compared to synthetic polymers, which can be mass-produced at a lower cost.
- Environmental Impact: Natural polymers have a lower environmental impact as they are biodegradable and come from renewable sources, while synthetic polymers contribute to plastic pollution and require fossil fuels for production.

