Introduction
Have you ever wondered why ice melts when heated or why a solid substance turns into a liquid at a certain temperature? These phenomena can be explained by two important concepts in thermodynamics: melting point and freezing point. In this article, we will explore the difference between these two terms and how they are related to the phase changes of matter.
What is the melting point?
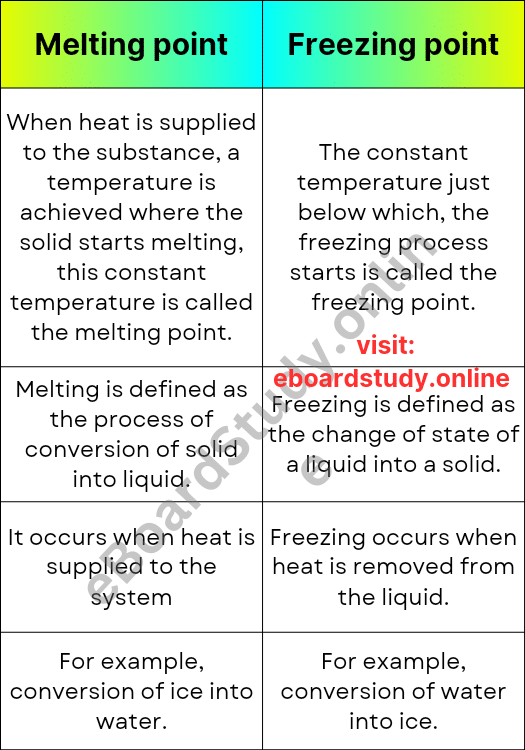
The melting point is the temperature at which a solid substance changes into a liquid state. It is the point at which the intermolecular forces holding the particles together weaken, allowing them to move freely and take on the shape of their container. For example, when you heat an ice cube, it gradually melts and turns into water.
What is a freezing point?
The freezing point is the temperature at which a liquid substance changes into a solid state. It is the point at which the particles in a liquid slow down and come together to form a more organized and rigid structure. For example, when you place a glass of water in the freezer, it eventually reaches its freezing point and solidifies into ice.
Key Differences
- Definition: The melting point is the temperature at which a solid substance changes to a liquid state, while the freezing point is the temperature at which a liquid substance changes to a solid state.
- The direction of change: the melting point involves a change from solid to liquid, whereas the freezing point involves a change from liquid to solid.
- Energy Exchange: During melting, energy is absorbed as heat to break the intermolecular forces, while during freezing, energy is released as heat when the intermolecular forces are formed.
- Equilibrium: At the melting point, both solid and liquid phases coexist in equilibrium, whereas at the freezing point, only the solid phase is present.
- Temperature Range: The melting point of a substance is typically higher than its freezing point. This is because the energy needed to break the intermolecular forces is greater than the energy released when they are formed.
