Introduction
Genotype and phenotype are vital concepts in the subject of genetics. They assist us understand the complicated relationship between an organism’s genetic information and its observable trends. In this text, we are able to discover the distinction among genotype and phenotype with the assist of two tables. These tables will provide a clear comparison, highlighting the contrasting features of genotype and phenotype. So allow’s dive into the captivating global of genetics and unravel the mysteries in the back of genotype and phenotype.
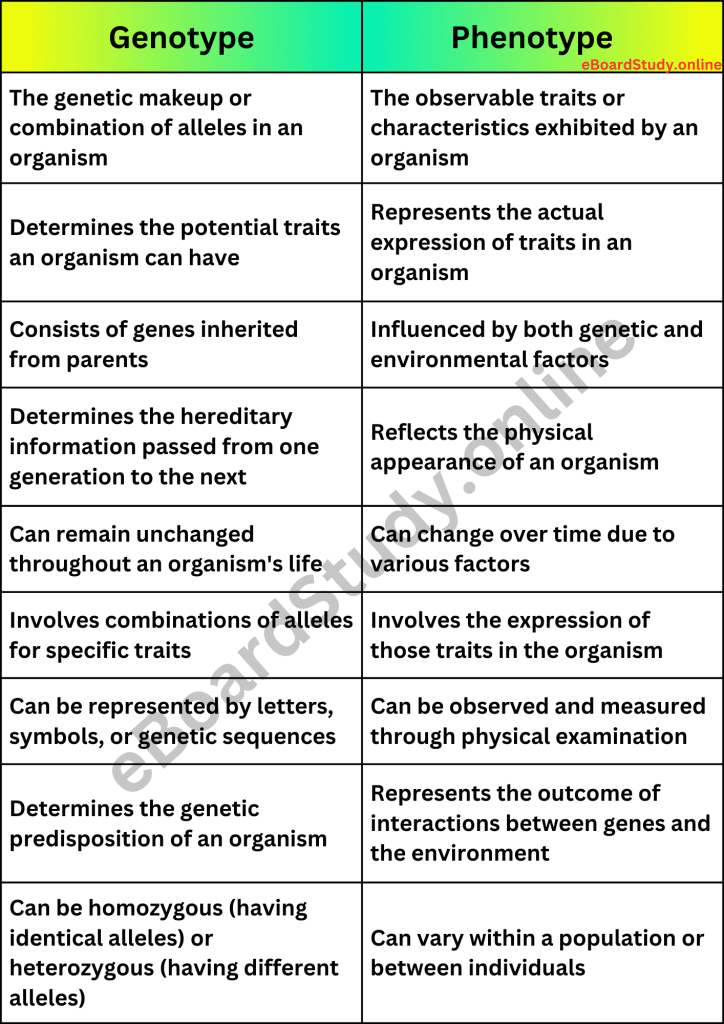
Difference Between Genotype and Phenotype with Example: Explained in Two Table Form
What is the difference among genotype and phenotype?
Genotype refers back to the genetic makeup of an organism, which accommodates the combination of alleles inherited from its dad and mom. On the other hand, phenotype represents the observable traits or characteristics exhibited through an organism, on account of the expression of its genes and the affect of environmental factors.
How do genotype and phenotype relate to each other?
Genotype determines the potential traits an organism can have, while phenotype represents the actual expression of those traits. Genotype acts as the blueprint, providing the instructions for the development and functioning of an organism, while phenotype reflects the physical manifestation of those instructions.
How are genotype and phenotype influenced?
Genotype is primarily influenced by the alleles inherited from parents, as well as genetic mutations that may occur. Phenotype, then again, is prompted through each genetic elements and the environment in which an organism develops. The interaction between genes and the surroundings plays a full-size position in determining an organism’s phenotype.
Can genotype and phenotype change over time?
Genotype generally remains unchanged throughout an organism’s life, except for rare instances of genetic mutations. In evaluation, phenotype can alternate over time due to various factors along with growing older, improvement, environmental affects, and lifestyle picks. For instance, someone’s height may also increase as they undergo early life.
How are genotype and phenotype represented?
Genotype can be represented by letters, symbols, or genetic sequences that denote the specific alleles an organism possesses. Phenotype, on the other hand, is observed and measured through physical examination. It encompasses various traits, including physical appearance, behavior, and physiological characteristics.
Can genotype and phenotype vary within a population?
Yes, both genotype and phenotype can exhibit variation within a population or between individuals. In a population, extraordinary mixtures of alleles can deliver upward push to numerous genotypes, ensuing in more than a few phenotypes.This genetic diversity contributes to the overall variation observed in traits within a species.
Conclusion:
Understanding the difference between genotype and phenotype is vital for comprehending the complexities of genetics. Genotype represents the genetic makeup of an organism, while phenotype encompasses its observable traits. The tables supplied in this article have outlined the dissimilarities between genotype and phenotype, shedding light on their wonderful traits. By grasping the nuances of genotype and phenotype, we benefit a deeper perception into the captivating world of genetics.
FAQ
Most frequent questions and answers
Yes, genotype provides the foundation for phenotype expression. However, environmental factors can also influence phenotype. The interaction between genes and the environment determines the final observable traits.
No, both genetic and environmental factors contribute to the expression of traits. While genotype sets the potential range of traits, the environment plays a significant role in shaping how those traits manifest.
While certain observable traits can provide clues about an organism’s genotype, a direct determination of genotype usually requires genetic testing or analysis. Phenotype alone might not offer a whole picture of an organism’s genetic make-up.
Yes, two organisms can have different genotypes yet exhibit the same phenotype. This phenomenon is known as phenotypic plasticity, where a couple of genotypes can result in comparable observable traits because of the have an impact on of environmental factors.
In most cases, genotype remains consistent within an individual. However, certain genetic conditions or mutations can result in mosaicism, where different cells within an organism may possess distinct genotypes, leading to variations in phenotype.
Studying genotype and phenotype gives treasured insights into the mechanisms of inheritance, genetic diseases, evolutionary strategies, and the effect of environmental factors on organisms. It aids in understanding the complexities of genetics and advancing various fields of research.
